How to customise a DIAB template to select a data transformation tool
Step 1: Select your agency’s reference architecture
DIAB taps on GovTech DSAID’s experience with multiple government projects to offer reference architecture as templates. These templates can help agencies speed up their infrastructure architecture creation process, especially for typical agency use cases.
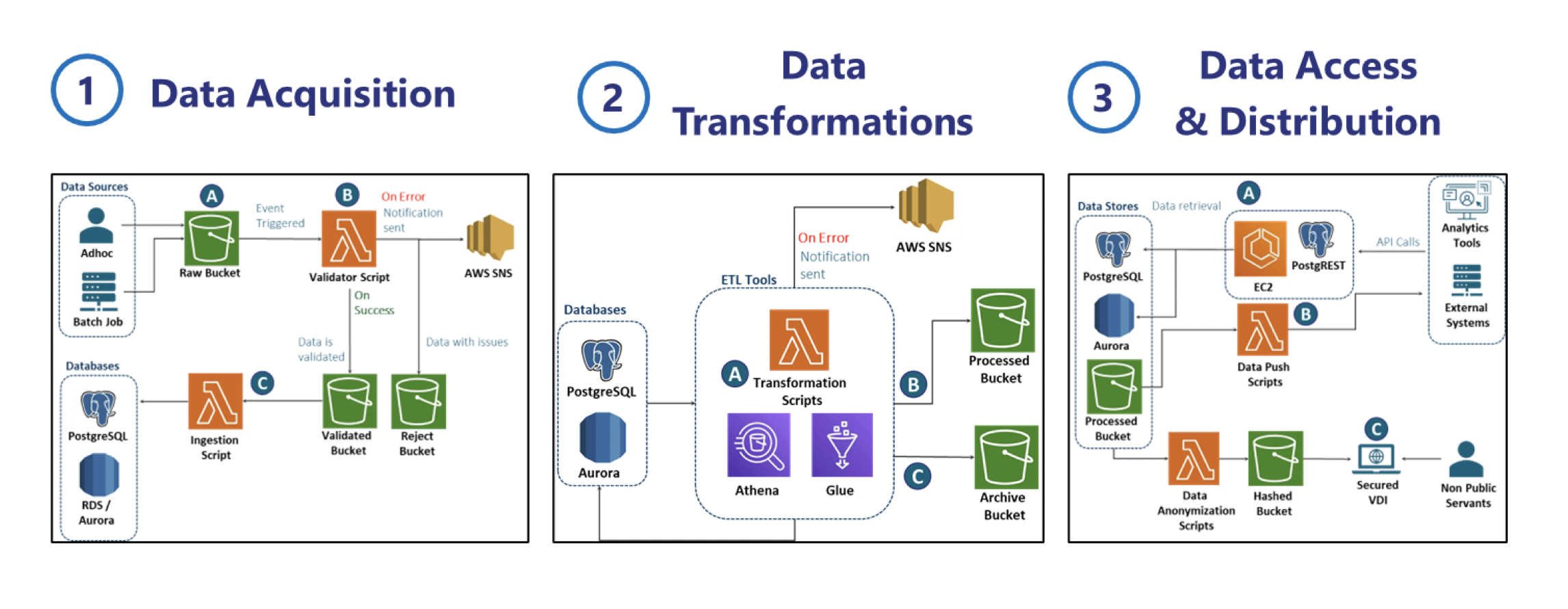
As seen in Fig 3, the DIAB reference architecture templates help agencies to quickly select what cloud resources they wish to use, and also save them the hassle of designing infrastructure architecture from scratch.
After selecting the relevant template, your agency should consult your Solution Architect to ensure that the DIAB template fits your use case and conforms to the agency’s architecture standards. Agency Solution Architects should provide the necessary guidance and approve the final architecture.
Step 2: Customising DIAB for your agency use case
Agencies that wish to customise DIAB’s reference architecture to fit their use case are free to do so.
Fig 4 depicts a common use case of selecting a data transformation tool, and illustrates how an agency can use DIAB’s reference architecture template and customise it to fit their needs.
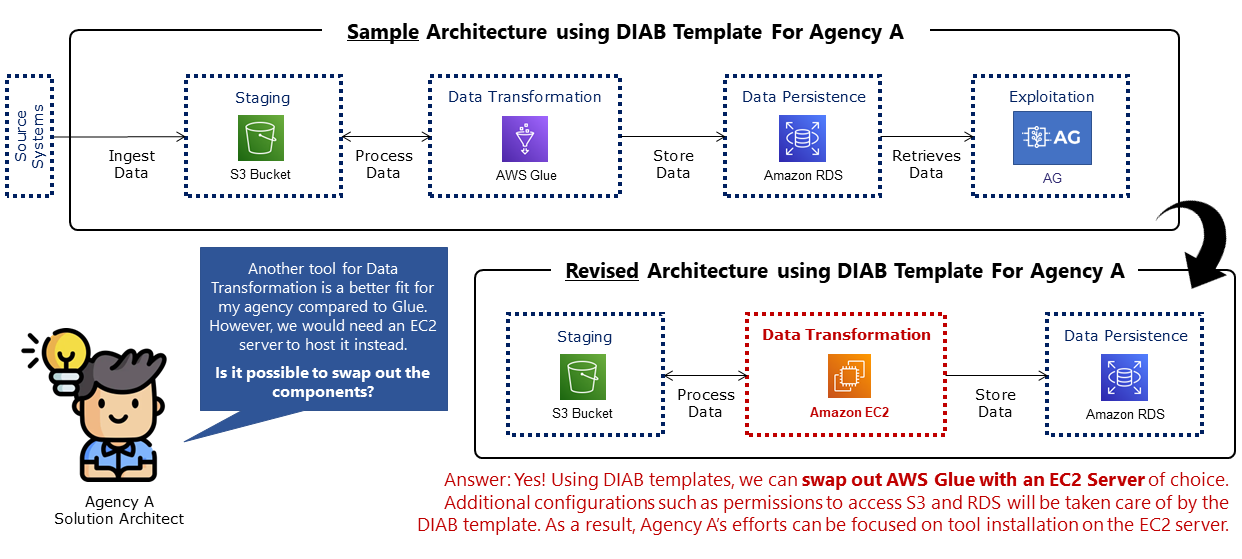
Step 3: Deploying DIAB
Deploying DIAB is simple. For instance, spinning up an RDS Database, which is a managed SQL database service provided by AWS, normally requires agencies to create the following resources:
- Key Management Service (KMS) Keys used to encrypt, decrypt and re-encrypt data
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Policies to allow or deny users from performing certain actions
- Database (DB) Parameters that specify how the database is configured e.g. the amount of resources, memory etc.
- Security Group, which acts as a virtual firewall that controls incoming/outgoing traffic
- Secrets Manager, which rotates, manages and retrieves database credentials, API keys and more
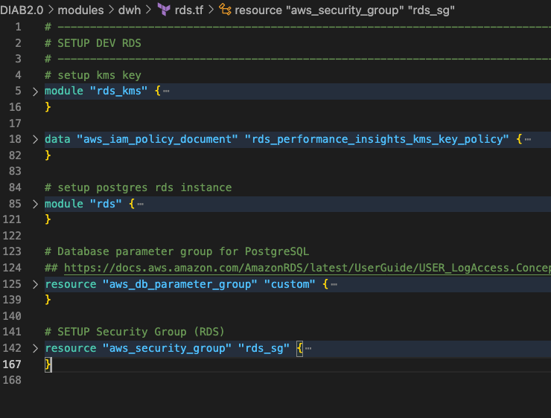
Agencies can now take a DIAB script template, fill in some variables – such the networking variables, project name, and secrets – and deploy immediately to their GCC environment.
This process is easily replicable across all environments (Dev-UAT-Prod). Agencies that want to deploy DIAB in-house can refer to the DIAB Gitlab repository for information and documentation on DIY deployment.
Vendors are allowed to deploy DIAB, but their usage is subject to the DIAB Terms of Use. However, agencies should ensure that the vendors read and comply with the Terms of Use.
For more information about deploying DIAB via DSAID engagement, please contact the team through this form.
Last updated 02 August 2023
Thanks for letting us know that this page is useful for you!
If you've got a moment, please tell us what we did right so that we can do more of it.
Did this page help you? - No
Thanks for letting us know that this page still needs work to be done.
If you've got a moment, please tell us how we can make this page better.

